Helping Ensure Compliance with Room Pressure Standards

How Healthcare Facilities Maintain Safe and Controlled Environments
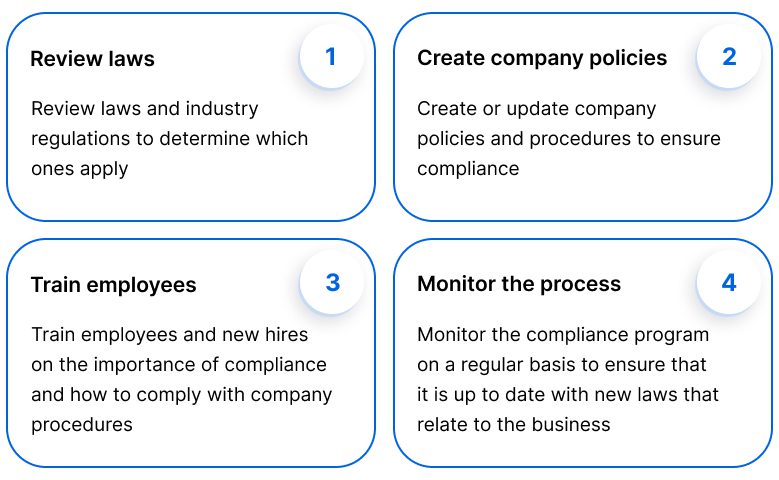
Maintaining proper room pressure is critical in healthcare settings, as it helps control the spread of airborne pathogens and protects both patients and healthcare workers. Compliance with room pressure standards requires careful planning, regular monitoring, and adherence to guidelines set by organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the American Society for Healthcare Engineering (ASHE), and the Facility Guidelines Institute (FGI). In this article, we’ll explore how healthcare facilities ensure that they meet these standards, safeguard patient care, and maintain a controlled environment.
- Positive pressure is typically used in areas like operating rooms, nurseries, and sterile processing departments to keep airborne contaminants out.
- Negative pressure is critical for isolation rooms where patients with airborne infectious diseases are treated, containing contaminants to prevent them from escaping into other parts of the facility.
- CDC Guidelines: The CDC’s “Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Health-Care Facilities” emphasize the importance of maintaining pressure differentials in certain rooms, particularly in isolation areas and sterile environments.
- ASHE Guidelines: The American Society for Healthcare Engineering provides technical standards for managing hospital HVAC systems, helping facilities design and maintain effective air pressure systems.
- FGI Guidelines: The Facility Guidelines Institute sets standards for the construction of healthcare facilities, including requirements for room pressure differentials to promote patient safety and infection control.
- Automated alarms: When pressure levels deviate from the required standards, the system automatically triggers alarms, notifying staff of the issue. This allows for immediate corrective action, minimizing risks to patient safety.
- Remote monitoring: Advanced systems can also integrate with facility management platforms, allowing for centralized monitoring of room pressures across the entire hospital. This enables maintenance teams to detect and resolve problems remotely before they compromise patient safety.
- Ventilation adjustments: HVAC systems are adjusted regularly to meet the requirements of different spaces. For example, in negative pressure isolation rooms, the ventilation system is designed to remove more air from the room than is supplied, creating a vacuum that prevents airborne contaminants from escaping.
- Filtration: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are often used in both positive and negative pressure environments to ensure that contaminants are either removed from or prevented from entering the room.
- Pressure differential testing: HVAC specialists use specialized equipment to measure the pressure differential between rooms to ensure the system is functioning as designed.
- Airflow verification: Airflow patterns are checked to confirm that air is moving in the correct direction (e.g., from clean areas to less clean areas in positive pressure rooms, or into the isolation room in negative pressure setups).
- Protocols for entering/exiting rooms: Clear protocols are established for entering and exiting positive and negative pressure rooms to avoid disrupting airflow. For example, healthcare workers must ensure that doors are properly sealed in negative pressure isolation rooms to maintain containment.
- Emergency procedures: Staff are trained to follow specific procedures in case of pressure failures, including contacting maintenance teams and implementing temporary safety measures like portable HEPA filtration systems.
Conclusion
Healthcare facilities ensure compliance with room pressure standards through a combination of continuous monitoring, HVAC system management, regular audits, and staff training. By adhering to guidelines from the CDC, ASHE, and FGI, hospitals can maintain the required pressure differentials that are critical for infection control. This vigilance helps prevent the spread of airborne pathogens, ensuring a safe environment for both patients and healthcare workers.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). “Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Health-Care Facilities.” 2003. Link
- American Society for Healthcare Engineering (ASHE). “Hospital Airborne Infection Isolation Room (AIIR) Guidance.” 2013.
- Facility Guidelines Institute (FGI). “Guidelines for Design and Construction of Hospitals and Outpatient Facilities.” 2022. [Link](https://fgiguidelines.org/guidelines/2022
Related Resources
Preventing Infection with Hospital Monitoring and Control
Preventing Infection with Hospital Monitoring and Control
If you are involved with designing, building, or remodeling critical spaces for hospitals and laboratories, you can access TSI papers and guides on room pressure management.
How Does Continuous Room Pressure Monitoring Enhance Patient Safety and Infection Control?
Room pressure monitoring is essential to maintaining a safe healthcare environment.
The Critical Role of Positive and Negative Room Pressures in Helping Prevent Airborne Infections in Hospitals
These controlled pressure environments are vital to ensuring patient safety, minimizing hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), and protecting healthcare workers.
TSI Incorporated
500 Cardigan Road
Shoreview, Minnesota 55126 USA
Call Us
800-680-1220/ +1 651-490-2860
Other TSI Online Properties
Does A Bathroom Push Air In Or Pull Air Out? Exploring The Ventilation System In Bathrooms

Have you ever wondered how the air in your bathroom seems to disappear so quickly after taking a shower? It’s not magic or a prank; it’s all thanks to the ventilation system in your bathroom. But did you ever wonder whether the bathroom pushes the air out or pulls it in? Well, get ready to dive into the world of bathroom ventilation as we explore whether it’s a push or pull mechanism.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Air movement | Push or pull |
| Purpose | Ventilation |
| Source of air | Inside or outside |
| Operation mechanism | Fan or exhaust system |
| Location of air intake | Bathroom or adjacent room |
| Noise level | Varies (low to high) |
| Energy consumption | Varies (low to high) |
| Size/CFM rating | Varies (small to large) |
| Maintenance requirements | Regular cleaning |
| Odor removal | Yes |
| Humidity control | Yes |
| Mold/mildew prevention | Yes |
| Condensation prevention | Yes |
| Cost | Varies (affordable to expensive) |
| Installation method | Wall or ceiling mounted |
| Control options | Manual or automatic |
| Timer function | Yes |
| Efficiency | Varies (low to high) |
| Safety features | Overheating protection, moisture-resistant materials |
| Aesthetics | Various designs and finishes |
| Durability | Varies (low to high) |
| Warranty | Varies (short to long) |
Explore related products
What You’ll Learn
- Does a bathroom push air in or pull air out?
- How does a bathroom extraction fan work?
- What is the purpose of a bathroom exhaust fan?
- Can a bathroom exhaust fan help improve air quality?
- Should a bathroom fan be left on all the time or only when necessary?
Does a bathroom push air in or pull air out?

Source: www.hansgrohe.com
There is often confusion and debate regarding whether a bathroom pushes air in or pulls air out. To understand this concept, we need to delve into the physics of air flow and the mechanics of a bathroom ventilation system. In this article, we will break down the mechanism behind how a bathroom moves air and whether it pushes air in or pulls air out.
Firstly, it is important to note that a well-ventilated bathroom is essential for maintaining good indoor air quality and preventing the accumulation of harmful pollutants. A ventilation system in a bathroom typically consists of an exhaust fan and a ductwork system. The purpose of this system is to remove odors, moisture, and pollutants from the bathroom and expel them to the outside.
When the exhaust fan is turned on, it creates negative pressure within the bathroom. This negative pressure effectively pulls air out of the bathroom. The exhaust fan sucks the air from the bathroom, which then travels through the ductwork system and is eventually expelled outside.
To better understand this process, let’s go through the step-by-step mechanism of how a bathroom ventilation system works:
- When the exhaust fan is activated, it begins to rotate, creating a low-pressure area within the bathroom.
- The lower air pressure in the bathroom causes air from the surrounding areas to rush into the room to equalize the pressure.
- As air rushes into the bathroom, it displaces the stale air, odors, and moisture present in the room.
- The exhaust fan then captures the air and directs it through the ductwork.
- The ductwork provides a pathway for the air to travel from the bathroom to the outside.
- Once outside, the expelled air dissipates into the atmosphere, completing the ventilation process.
It is crucial to note that during the ventilation process, fresh air from adjacent rooms or outside sources replaces the air that is being removed from the bathroom. This constant influx of fresh air ensures that the bathroom remains effectively ventilated, preventing the buildup of humidity and pollutants.
In summary, a bathroom exhaust fan creates negative pressure within the bathroom, resulting in air being pulled out of the room. This process effectively removes odors, moisture, and pollutants from the bathroom and replaces them with fresh air. The ventilation system in a bathroom pulls air out rather than pushing it in.
Overall, understanding the mechanics of a bathroom ventilation system can help homeowners ensure proper airflow and maintain a healthy environment in their bathrooms. Regular maintenance of the exhaust fan and proper cleaning of the ductwork is essential to ensure optimal air circulation. By keeping the bathroom well-ventilated, you can create a more pleasant and hygienic environment for yourself and your family.
How to Repair a Bathroom Vent
You may want to see also
How does a bathroom extraction fan work?

Source: www.homeclick.com
Bathroom extraction fans are an essential and commonly used appliance in many homes. They help remove moisture, odors, and pollutants from the bathroom, improving air quality and promoting a healthier environment. But have you ever wondered how exactly these fans work?
The basic principle behind a bathroom extraction fan is relatively straightforward. The fan is mounted on the ceiling or wall of the bathroom and is connected to a duct that leads outside. When the fan is turned on, it creates a negative pressure within the bathroom, which causes air to be drawn out through the duct and expelled outside. This process effectively removes stale air, moisture, and odors from the bathroom and replaces them with fresh air from outside.
Let’s take a closer look at the key components and steps involved in the operation of a bathroom extraction fan:
- Fan Motor: The heart of the extraction fan is its motor. When the fan is activated, the motor spins the blades, generating airflow and suction.
- Ductwork: The fan is connected to a flexible or rigid duct that directs the extracted air outside the building. The duct should be properly installed to ensure an airtight connection, preventing any leakage of air or condensation buildup.
- Louvers or Grilles: To protect the fan from debris and insects, a louver or grille is installed on the exterior end of the duct. This prevents any unwanted objects from entering the duct and potentially causing blockages or damage to the fan.
- Switches and Controls: Most bathroom extraction fans have a simple on/off switch located within the bathroom. Some advanced models may include additional features such as timers, humidity sensors, or adjustable fan speed controls.
- Ventilation Requirements: It is important to ensure that the extraction fan is appropriately sized for the bathroom. The fan needs to have sufficient power to effectively remove the moisture and odors present in the space. The required ventilation rate is typically based on the size of the bathroom, and industry guidelines should be followed to determine the appropriate fan size.
- Maintenance: Like any appliance, a bathroom extraction fan requires regular maintenance to operate optimally. This includes cleaning the fan blades and grilles periodically to remove dust and debris that may accumulate over time. It is also important to check the ductwork for any signs of damage or blockages and address them promptly.
To further illustrate how a bathroom extraction fan functions, let’s consider an example. Imagine you’ve just finished taking a hot shower, and the bathroom is filled with steam and condensation on the mirror. You turn on the extraction fan, and within a few minutes, the steam and condensation start to dissipate. The fan creates negative pressure, drawing the moisture-laden air out of the bathroom through the duct, and replacing it with fresh air from outside. This process helps prevent the growth of mold and mildew, which thrive in moist environments.
In conclusion, a bathroom extraction fan works by creating negative pressure and extracting air from the bathroom, removing moisture, odors, and pollutants. Understanding how these fans work can help homeowners better appreciate their importance in maintaining a healthy and comfortable bathroom environment. Regular maintenance and proper ventilation sizing are key to ensuring the optimal performance of a bathroom extraction fan.
Exploring the Necessity of Bathrooms in Rustic Cabins at Pennsylvania State Parks
You may want to see also
What is the purpose of a bathroom exhaust fan?

Source: www.thespruce.com
Bathroom exhaust fans are an essential part of any bathroom ventilation system. Their primary purpose is to remove moisture, odors, and pollutants from the air, ensuring proper indoor air quality and preventing the build-up of mold and mildew in the bathroom. In addition to removing these impurities, bathroom exhaust fans also help to maintain a comfortable and healthy environment by reducing humidity levels and preventing the spread of unpleasant smells.
Excessive moisture in the bathroom can lead to a range of problems. It can cause mold and mildew to grow on surfaces such as walls and ceilings, leading to health issues, including respiratory problems and allergies. Moisture can also damage fixtures and furniture in the bathroom, such as wood cabinets and mirrors. By removing excess moisture from the air, bathroom exhaust fans help to prevent these issues, ensuring a clean and healthy living environment.
In terms of air quality, bathroom exhaust fans remove odors, toxins, and pollutants from the bathroom air. These can include fumes from cleaning products, hair sprays, and other personal care products. By eliminating these odors and pollutants, bathroom exhaust fans contribute to a more pleasant and comfortable bathroom experience.
So, how does a bathroom exhaust fan actually work? The process is relatively straightforward. When the fan is turned on, it creates a negative pressure inside the bathroom. This negative pressure causes air from the bathroom to be drawn into the fan. As the air passes through the fan, it is filtered and then expelled outside through a vent or duct connected to the fan. The replacement air for the bathroom is then drawn in from other areas of the house, ensuring a constant flow of fresh air.
It’s important to note that bathroom exhaust fans should always be vented to the outside of the house, rather than into an attic or crawl space. Venting the fan to the outside prevents the moisture and odors from being recirculated within the house, maintaining good indoor air quality throughout the home.
When it comes to choosing a bathroom exhaust fan, there are a few factors to consider. The fan should be appropriately sized for the bathroom, taking into account factors such as the size of the room and the number of fixtures present. A properly sized fan will effectively remove moisture and odors from the air without being too loud or consuming excessive energy.
Another consideration is the fan’s ventilation rate, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). The ventilation rate should be sufficient to remove moisture and odors from the bathroom in a reasonable amount of time. A general rule of thumb is to have a fan with a ventilation rate of at least one CFM per square foot of bathroom floor area.
In conclusion, the purpose of a bathroom exhaust fan is to remove moisture, odors, and pollutants from the air in the bathroom, ensuring a comfortable and healthy living environment. By properly sizing and venting the fan, homeowners can effectively control humidity levels, prevent the growth of mold and mildew, and maintain good indoor air quality. So, make sure to install a bathroom exhaust fan in your bathroom to enjoy a fresh and clean space.
Accessible Air Travel: Ensuring a Restroom Solution for Wheelchair Users on Planes
You may want to see also
https://tsi.com/healthcare/learn/helping-ensure-compliance-with-room-pressure-standards/https://shunshelter.com/article/do-bathroom-push-air-in-or-pull-air-out